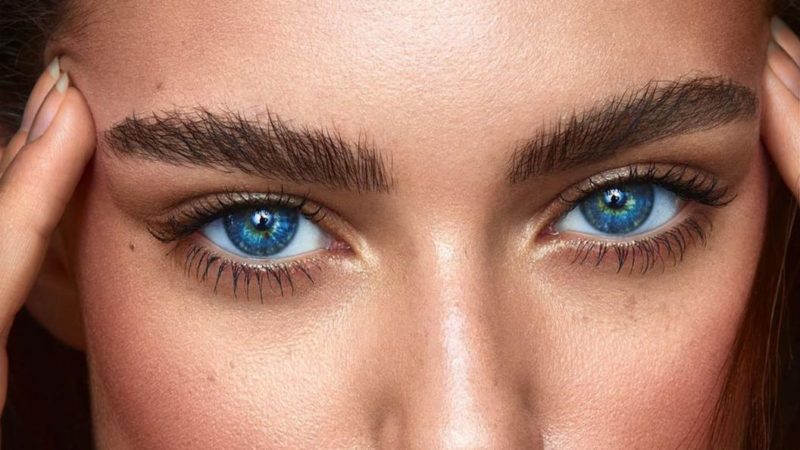
Why do men’s eyebrows get bushier with age, women’s do not?

Some older men’s huge eyebrows, extended ear hair, and thick sniffing locks seem to never stop growing. While many men lose their hair on the top of their heads, the hairs on their eyebrows, ears, and noses look like they’ve been bathed in a magical growing elixir.
Conversely, women’s hair, including eyebrows, tends to thin out with age. So why do men’s various facial hairs often get thicker in old age, while women’s hair doesn’t?
However, where hair grows, how fast it grows and its texture and color are primarily based on genetics, age, nutrition, health and sex, said Dr. Marie Jhin, president of Premier Dermatology in San Carlos, California.
But as people get older, “hormones and various hormone responses are the main reason for the difference between males and females in hair,” Del Campo said.
How eyebrow hair grows?
All body hair grows from hair follicles. The life cycle of these follicles has three phases: the growth phase (anagen), the transition phase of two weeks (catagen) and the dormant phase of months (telogen). After the hair follicles go dormant, the hair eventually falls out, sometimes called the exogenous phase, according to the 2020 revision. The process then starts over from the anagen phase.
The shorter the anagen phase of a hair follicle, the shorter the hairs on that part of the body are when they hibernate. “The eyebrows have a very short anagen phase of about 30 days, that’s all,” Del Campo said. This short period of growth is followed by a prolonged resting phase, which explains why eyebrow hair is typically only 0.4 inches (1 centimeter) or less.
“If the anagen phase were longer, people would have to use barber scissors to trim their eyebrows very frequently,” Del Campo said, grooming requirements that become necessary for some men as they age.
The role of testosterone
The duration of the different phases is influenced by the hormones that circulate in the body. “The hair cycle, as well as the structure of the hair follicle, are heavily influenced by various hormones,” Jhin told Live Science in an email. In particular, men often have high androgen levels, especially testosterone, while women tend to have lower androgen levels. These androgens are the reason men’s hair grows faster, she added.
During puberty, these androgens are responsible for hair growth in places such as the face, arms and back, according to the 2020 review. “These androgens work on specific parts of the body such as the pubis, chest, face and back. axillary areas [ ascelle] during puberty, “Jhin said.” They act as a stimulation for the hair.
As men age, some hair follicles become more sensitive to these hormones over time, according to Jhin. As the follicles become more sensitive to androgens, hormones keep them in the anagen phase longer, leading to more hair growth with age in places like the eyebrows, nose and ears.
Interestingly, somehow mysteriously, the hair follicles on the scalp react differently to testosterone, effectively shortening their growth cycle as testosterone levels rise, according to Jhin. That’s why some older men have shaggy eyebrows, long nose hair, and wispy ear hair, but a bald head.
“Men’s eyebrows tend to continue growing into old age (and this also applies to ear and nose hair),” Del Campo said. “In women, there are lower levels of testosterone.”
As women age, estrogen levels drop during menopause. Lower estrogen levels and other hormonal changes and factors in older age are believed to lead to thinner and less dense hair, according to the 2020 review. “As men continue to produce androgens into their 70s,” Jhin said. , “female hormones are depleted with menopause around age 50”.








